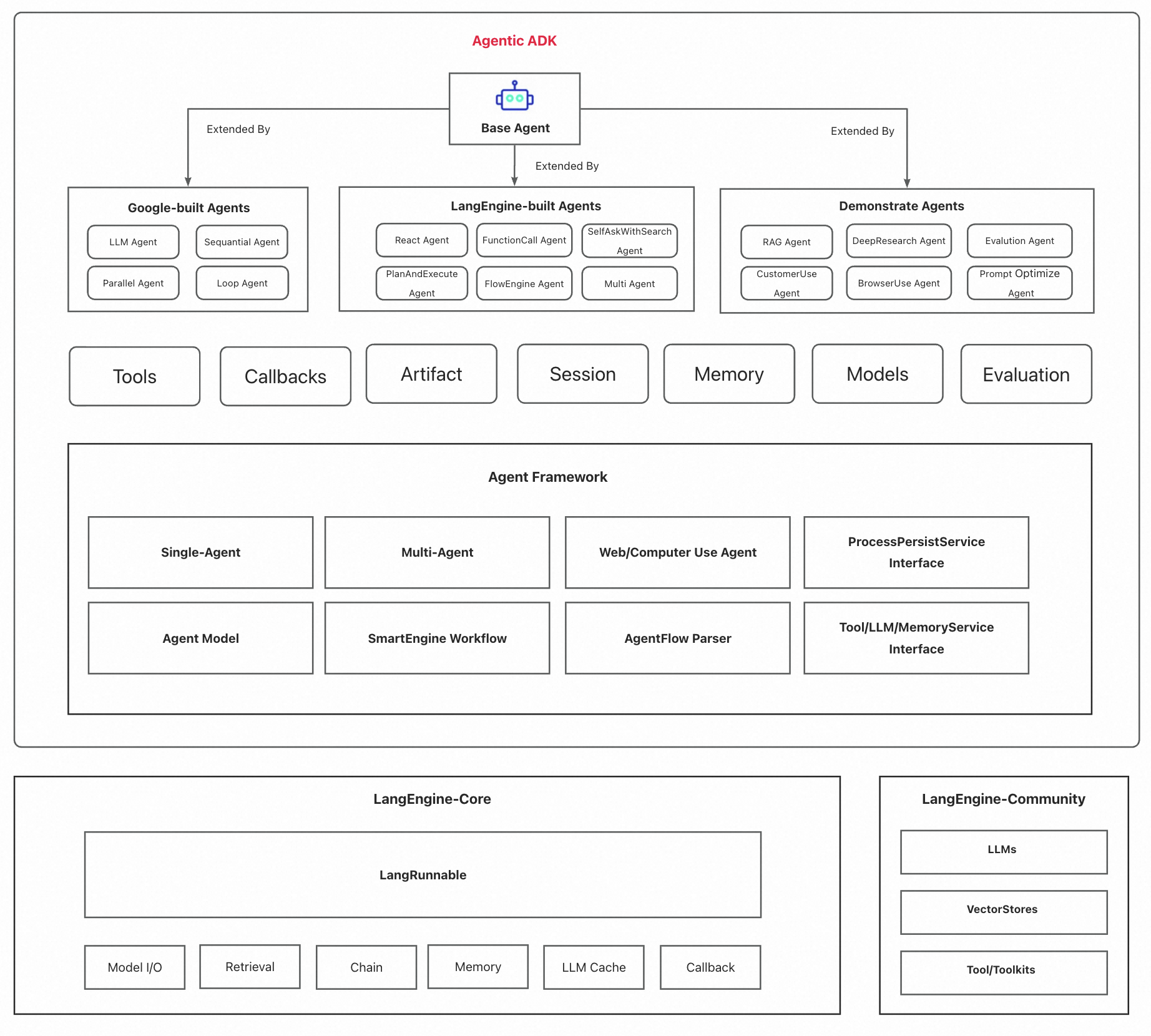
Agentic ADK is an Agent application development framework launched by Alibaba International AI Business, based on Google-ADK and Ali-LangEngine.
Agentic ADK is an Agent application development framework launched by Alibaba International AI Business, based on Google-ADK and Ali-LangEngine. It is used for developing, constructing, evaluating, and deploying powerful, flexible, and controllable complex AI Agents. ADK aims to make Agent development simpler and more user-friendly, enabling developers to more easily build, deploy, and orchestrate various Agent applications ranging from simple tasks to complex collaborations.
Features Overview
- Based on the Google ADK interface, it strengthens core execution pathways such as streaming interaction and visualization debugging tools, enabling developers to efficiently develop Agent applications.
- Seamlessly integrates with Alibaba's International Multimodal Large Language Model, Ovis, to achieve deep alignment and fusion of visual and textual information. This model is characterized by high performance and lightweight design, offering the following advantages for efficient development and deployment of multimodal Agents:
- Outstanding Logical Reasoning: By combining instruction fine-tuning and preference learning, the model's Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning abilities are significantly enhanced, enabling it to better understand and execute complex instructions.
- Precise Cross-Language Understanding and Recognition: Beyond just Chinese and English, the model has improved text recognition (OCR) capabilities in multilingual environments and optimized the accuracy of structured data extraction from complex visual elements such as tables and charts.
- Flexible multi-agent framework, supporting various execution modes such as synchronous, asynchronous, streaming, and parallel, and naturally integrating the A2A protocol.
- A high-performance workflow engine combined with agents, built on top of Alibaba's SmartEngine workflow engine, utilizes RxJava3 to implement a reactive programming model. It employs a node-based process system to define agent behaviors, supporting synchronous, asynchronous, and bidirectional communication modes, providing a flexible foundation for building complex AI applications.
- Offers hundreds of API tools and introduces the MCP integration gateway.
- DeepResearch/RAG, ComputerUse, BrowserUse, Sandbox, and other best practices for Agentic AI.
- Implementation of context extension for agent conversations, including Session, Memory, Artifact, and more, with built-in short and long-term memory plugins.
- Provides prompt automation tuning and security risk control-related agent examples.
Agentic ADK inherits the excellent design of google-adk and supports the following key features:
Rich large model selection. Natively compatible with the use of models/vendors including OpenAI, Bailian/Qwen, OpenRouter, Claude, etc.
| Component Abstraction | Description |
|---|---|
| LangEngine | This component supports all compatible third-party Model/WorkSpace integrations under the LangEngine ecosystem into the Agent system, including OpenAI, Bailian/Qwen, Idealab, OpenRouter, etc. |
| DashScopeLlm | Supports integration with OpenAPI interfaces on Alibaba Cloud Bailian |
Highly abstracted Agent definition and flexible Agent orchestration. The framework has built-in LLM/sequential/parallel/loop Agent definitions; supports single Agent and multi-Agent (MAS) architecture design, facilitating the expansion of your agent design patterns and architecture.
| Component Abstraction | Description |
|---|---|
| LlmAgent | A core component in ADK that acts as the "thinking" part of the application. It leverages the powerful capabilities of large language models (LLMs) for reasoning, understanding natural language, making decisions, generating responses, and interacting with tools. |
| SequentialAgent | A WorkflowAgent that executes its child Agents in the order specified in the list. |
| LoopAgent | A WorkflowAgent that executes its child Agents in a loop (i.e., iterative) manner. It repeatedly runs a set of agents until a specified iteration count is reached or a termination condition is met. |
| ParallelAgent | A WorkflowAgent that can execute its child Agents concurrently, significantly speeding up the entire workflow when subtasks can be executed independently. |
| Other Advanced Concepts | CustomAgents: Custom Agent processing flows can be implemented by inheriting google.adk.agents.BaseAgent. Multi-Agent Systems: Multiple different Agent instances can be combined into a multi-agent system (MAS), supporting the construction of more complex applications |
Rich tool assembly. Easy integration of Function/MCP and any third-party tools.
| Component Abstraction | Description |
|---|---|
| Function Tool | FunctionTool: Function as a tool, any method can be converted into a Tool for Agent to call. LongRunningFunctionTool: Designed for tasks that require significant processing time without blocking Agent execution. AgentTool: By orchestrating other Agents as tools, their capabilities in the system can be fully utilized. This tool allows the current Agent to call another Agent to perform specific tasks, effectively delegating responsibilities. |
| DashScopeTool | Integration with Alibaba Cloud Bailian tool applications |
| MCPTool | ADK built-in MCP tool |
| GoogleSearchTool | ADK built-in Google search tool |
| GUITaskExecuteTool | ADK built-in GUI task execution tool |
Flexible Callback mechanism. Provides hooks at multiple timing points during Agent execution, making it convenient to implement custom logic before and after LLM/Tool/Agent calls.
Reference: https://google.github.io/adk-docs/callbacks
Best Practices: https://google.github.io/adk-docs/callbacks/design-patterns-and-best-practices/
Out-of-the-box debugging and evaluation capabilities. Provides a white-screen Debug page for quick Agent debugging whether locally or remotely.
Built on Alibaba's SmartEngine workflow engine, it utilizes RxJava3 to implement reactive programming patterns, employs a node-based process system to define agent behavior, and supports synchronous, asynchronous, and bidirectional communication modes, providing a flexible foundation for building complex AI applications.
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ User Application Layer │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Runner (Execution Entry) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Pipeline Processing Layer │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Agent │ │ ... │ │ Custom Processing │ │
│ │ Execution │ │ │ │ Pipeline │ │
│ │ Pipe │ │ │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └────────────────┘ └─────────────────────────┘ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Flow Engine Layer │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ FlowCanvas │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ (Flow │ │ FlowNode │ │ DelegationExecutor │ │
│ │ Container) │ │ │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └────────────────┘ └─────────────────────────┘ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ AI Capability Abstraction Layer │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ BasicLlm │ │ BaseTool │ │ BaseCondition │ │
│ │ (LLM Model) │ │ (Tool Set) │ │ (Conditional Judgment) │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └────────────────┘ └─────────────────────────┘ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Infrastructure Layer │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ SmartEngine │ │ RxJava3 │ │ Spring Framework │ │
│ │ (Workflow │ │ (Reactive │ │ (Dependency Injection │ │
│ │ Engine) │ │ Programming │ │ Framework) │ │
│ │ │ │ Framework) │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └────────────────┘ └─────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
- FlowCanvas: The main container for flow definition, used to build and deploy workflows
- FlowNode: The base class for all flow nodes, defining the basic behavior of nodes
- Node Types:
LlmFlowNode: Used for interacting with large language modelsToolFlowNode: Used for executing external toolsConditionalContainer: Used for conditional branchingParallelFlowNode: Used for parallel executionReferenceFlowNode: Used for referencing other flows
- Runner: The main entry point for flow execution
- DelegationExecutor: Handles the execution of delegated tasks
- SystemContext: Contains execution context and configuration information
- Request/Result: Data structures for requests and responses
- BasicLlm Interface and Implementations (e.g.,
DashScopeLlm): Defines and implements interactions with large language models - LlmRequest/LlmResponse: Data structures for large language model interactions
- BaseTool Interface and Implementations (e.g.,
DashScopeTools): Defines and implements external tool calls
- PipeInterface: Interface for pipeline components
- AgentExecutePipe: Main implementation of the execution pipeline
- PipelineUtil: Utility class for pipeline execution
The framework supports three execution modes:
- SYNC (Synchronous Mode): Sequential execution, waiting for each node to complete before executing the next
- ASYNC (Asynchronous Mode): Asynchronous execution, can process multiple tasks in parallel
- BIDI (Bidirectional Mode): Supports bidirectional communication, can dynamically receive input
This project is licensed under Apache License Version 2 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.txt, SPDX-License-identifier: Apache-2.0).