-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Graphs ~ The heart of the database
From this article,
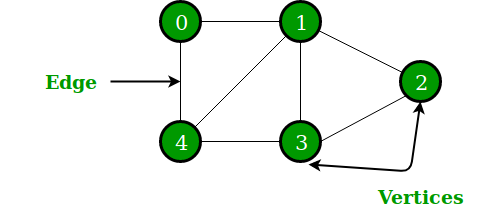
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of nodes and edges. The nodes are sometimes also referred to as vertices and the edges are lines or arcs that connect any two nodes in the graph. More formally a Graph can be defined as,
PS: The edges are also called relationships.
I recommend you read that full blog to know more about graphs.
There are 2 types of graphs:-
- SimpleGraph: Does not have explicit relation
- RelationalGraph: Has explicit relations.
In simplegaph, we need to pass the number of vertex our graph will have. In this example, There are only 4 vertex i.e A,B,C & X
SimpleGraph<String> graph = new SimpleGraph<>(4); // number of vertex
graph.addEdge("A", "B");
graph.addEdge("B", "C");
graph.addEdge("C", "A");
graph.addVertex("X");This will form a graph like this,
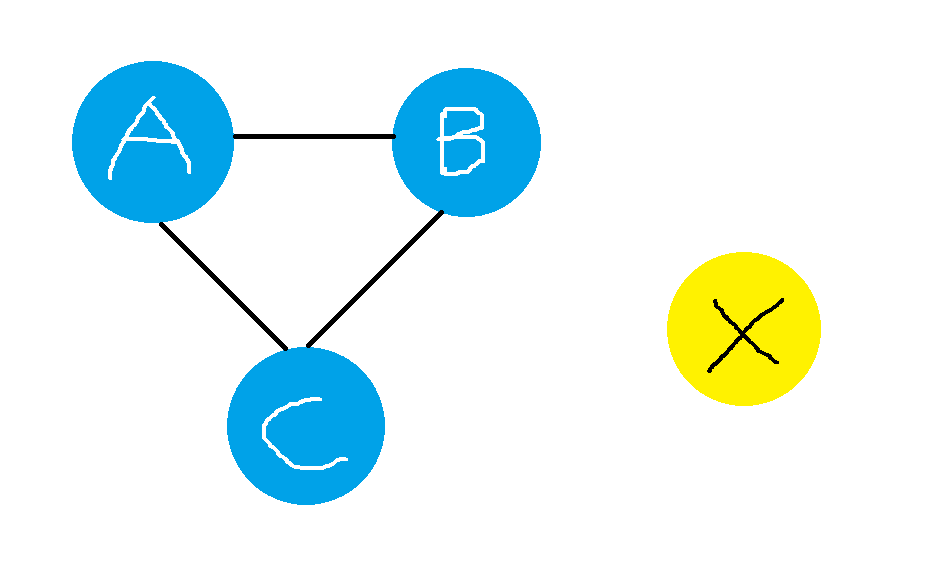
However, you cannot save this graph in the database. Database only allows graphs in which data implements the Savable interface. So you have to make a POJO which implements Savable in order to save it in the database.
Note: You cannot directly store primitives or String. You can only store Savable objects in this graph
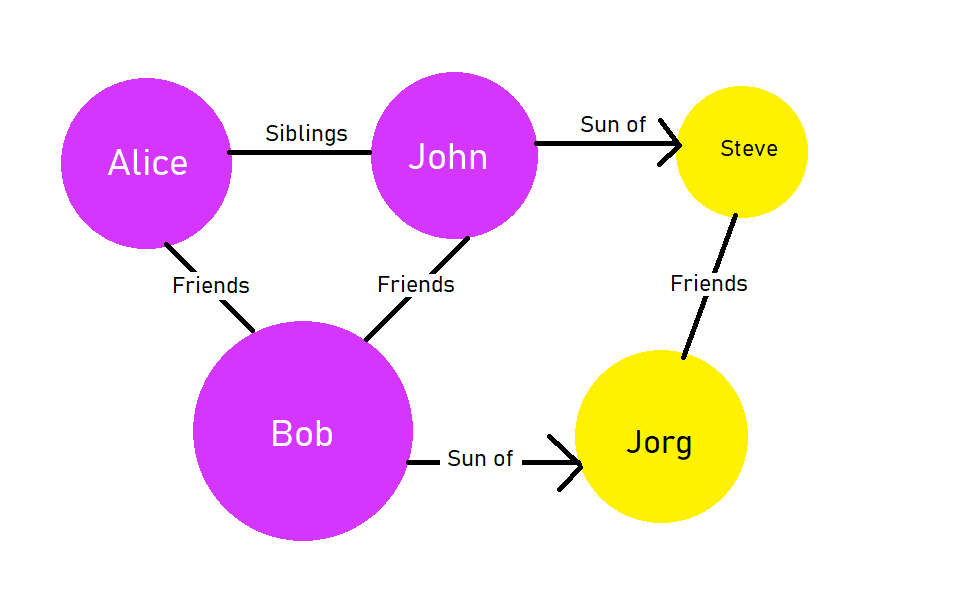
RelationalGraph<Person> graph = new RelationalGraph<>();
Person bob = new Person("Bob",15);
Person john = new Person("John",17);
Person alice = new Person("Alice",12);
Person steve = new Person("Steve",38);
Person jorg = new Person("Jorg",40);
graph.addEdge(bob,john, "friend");
graph.addEdge(john,bob, "friend"); // because both are friends
graph.addEdge(bob,alice, "friend");
graph.addEdge(alice,bob, "friend");
graph.addEdge(steve,jorg, "friend");
graph.addEdge(jorg,steve, "friend");
graph.addEdge(john,alice, "brother");
graph.addEdge(alice,john, "brother"); // siblings are bi-directional
graph.addEdge(jorg,steve, "son");
graph.addEdge(steve,jorg, "father");
graph.addEdge(bob,jorg, "son");
graph.addEdge(jorg,bob, "father");This will create a graph like this,
You can see the Person class code here
Here, we are using perosn name as their ID too.
We have already learnt to create graphs, it's now time to travel through them. Fortunately, you don't manually have to write an algorithm to do so. It had been already done by us. You have to use the conventional method. For example,
Tip: You can cast every object in the array to the type of data stored i.e Person in this case.
Object[] results = graph.search(person -> person.age < 20);
for (Object user: results)
System.out.println(user);Object[] results = graph.search(person -> person.name.equal("Alice"));
System.out.println(results[0])List<Person> neighbours = graph.getAdjacentVertices("Alice");
// or
List<Person> neighbours = graph.getAdjacentVertices("Bob");Here, "Alice" is the id of the Person returned by getId() method of the Savable class.
-
boolean hasEdge = graph.hasEdge("Alice","Bob")check if a relation exists between two nodes. -
boolean exist = graph.hasVertex("Steve");check if the graph contains the person -
List<Person> objs = (List<Person>) graph.getAllVertices()to get the data object from its id.
Every method of the Graph take the data object as the argument. But you might not always have the data, especially when you opened the graph from the database. So you can get the data by its id using this method and then can pass this in the methods.
That's all about the graph. Now you have mastered the graph data structure, Now if you don't have completed DSA yet, go for it. It will help you to create the best graph.