- VSCode (IDE)
- UV (Python Development Tool)
- Git (and GitHub)
-
Install WSL and VSCode by following these instructions. https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/remote/wsl
- Install the WSL with the Ubuntu distribution
-
Install UV on the WSL side (Do not install it on the Windows side)
Open an WSL terminal (Ubuntu), navigate to the
$HOMEdirectory, run the install script.cd ~ curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
-
Install VSCode for your OS. https://code.visualstudio.com/Download
-
Install UV (from the terminal)
cd ~ curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
Install git (from the terminal)
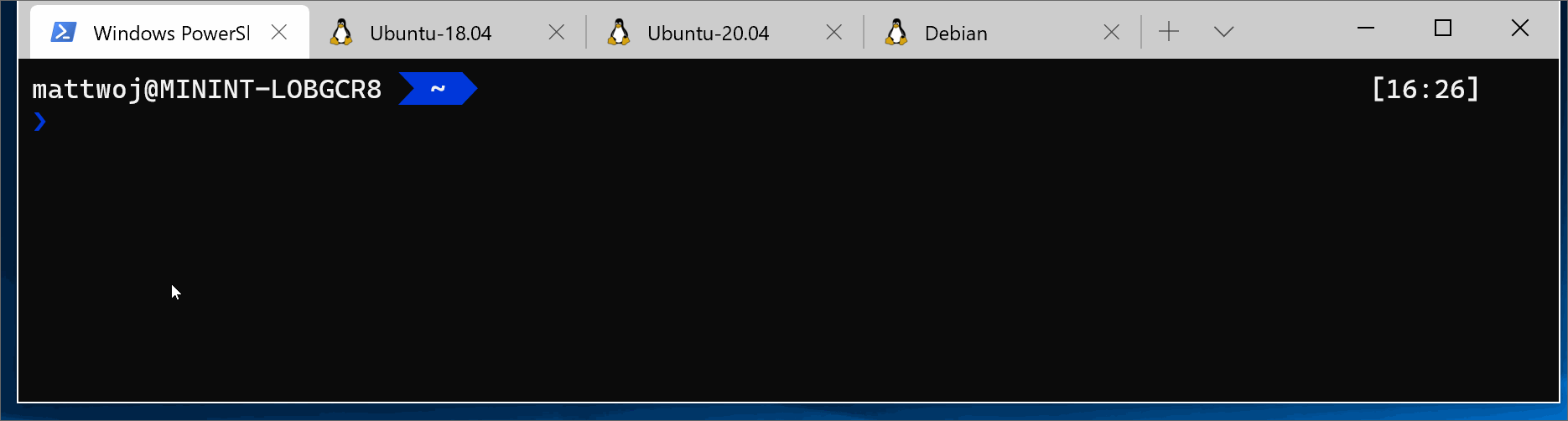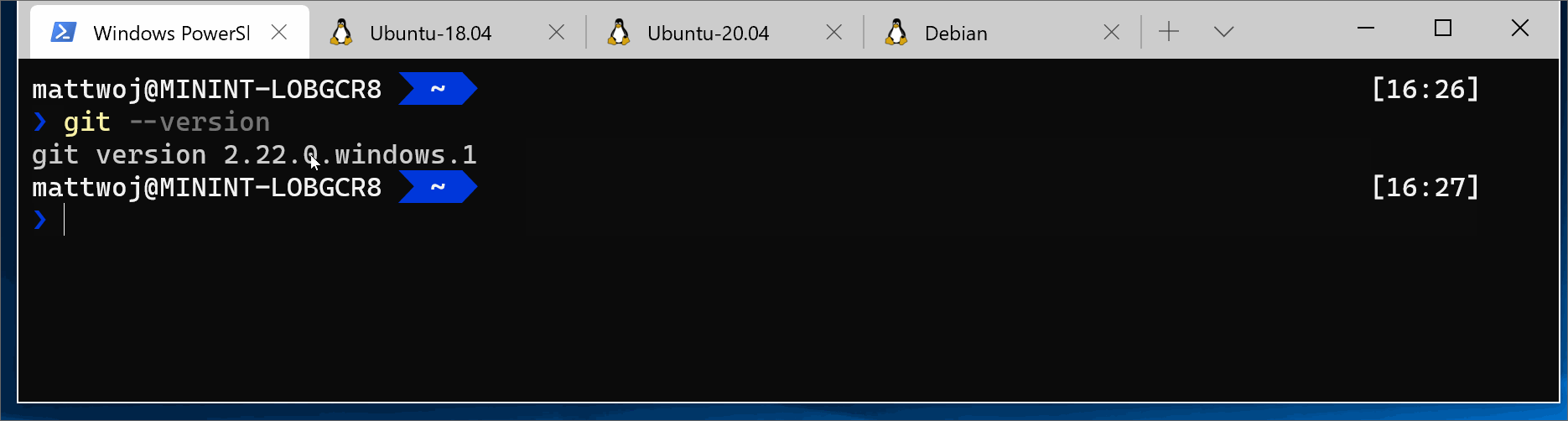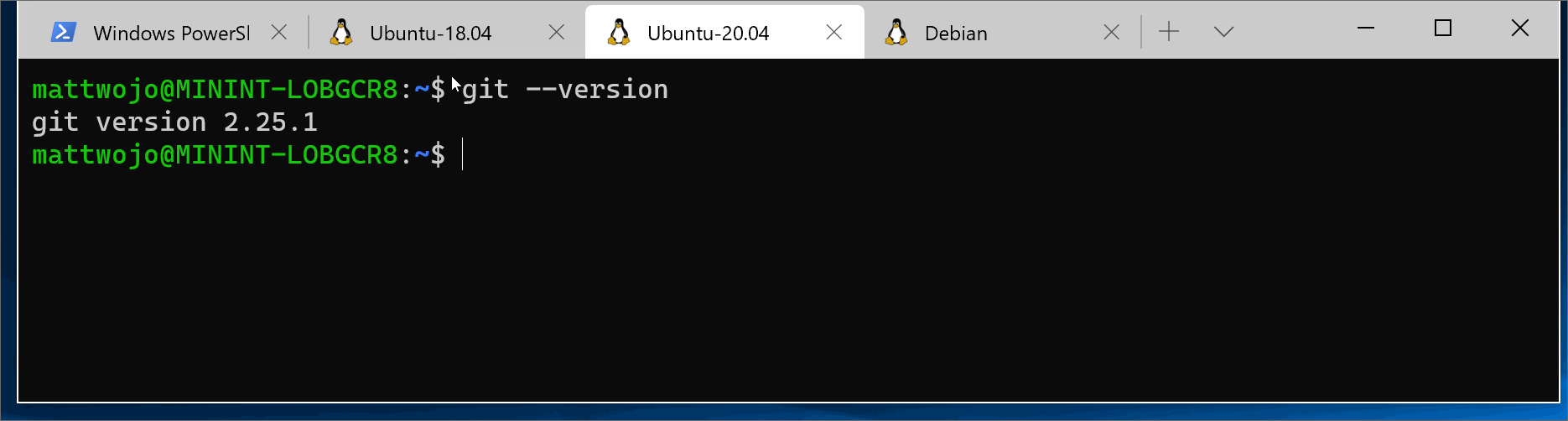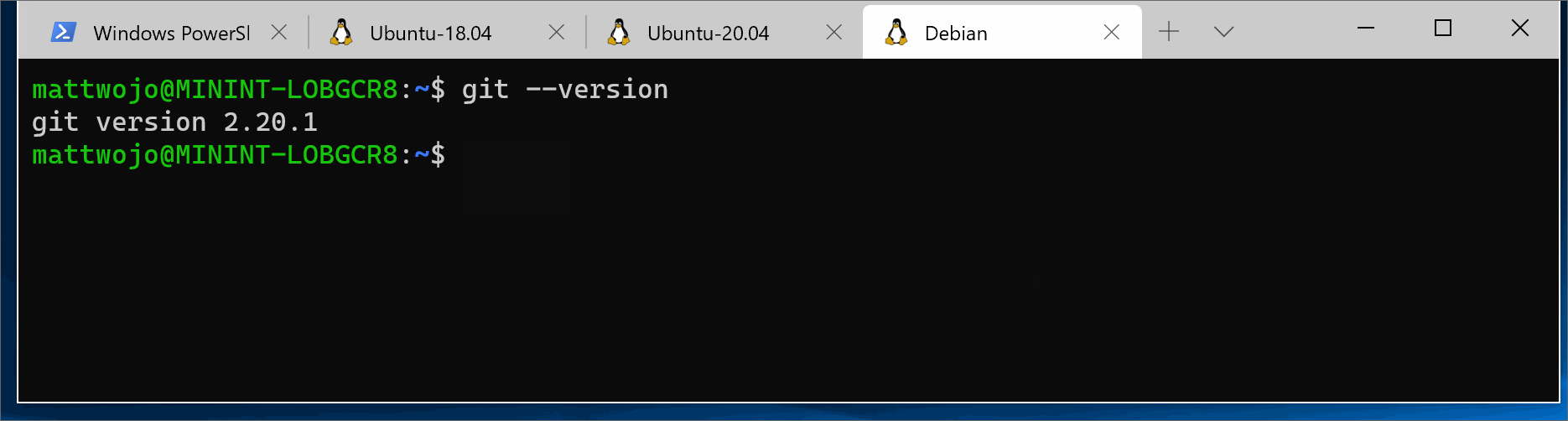
It is likely that git is already installed on your system. To check if you have git install, run this command in your terminal:
git --version(For WSL/Linux with an Ubuntu/debian distribution)
sudo apt install git-all (For MacOS, If you don't have brew, install it https://brew.sh/)
brew install git Open a terminal. Create a "projects" directory from your $HOME directory.
cd ~
mkdir projects/First, navigate to your projects folder
cd ~/projects/ From the browser, navigate to the GitHub repository for your project. Clone the project by clicking the green "Code" button. Select "HTTPS" and copy the line in the text box.
On your terminal, navigate to the projects folder and clone the repository.
cd ~/projects/
git clone https://github.com/chaconnb/NSC325_GROUP1.git # this is an exampleNavigate to the newly cloned repository and open VSCode from the repository root folder.
cd ~/projects/<your-repo-name>
code . With UV installed, you can set up the development environment by running this command in the project root directory:
uv syncThis will set up a Python virtual environment and install any dependencies listed in
the pyproject.toml. To activate the virtual environment on your terminal, run:
source .venv/bin/activate You can use VSCode to run Jupyter notebooks. Read the VSCode docs for more information. https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/datascience/jupyter-notebooks
You will need to set up the kernel. We suggest you use the local virtual environment we set up with UV. Follow these instructions on how to use your virtual environment in your
Jupyter notebook. VSCode should find and identify the project's virtual environment folder
and recommend it (i.e., it should be .venv/bin/python)